
Table of Contents
- Are temperature fluctuations in commercial refrigeration normal?
- How Important Is Temperature In Relation To Commercial Refrigeration?
- Observing Correct Temperatures for Different Foods
- Commercial Refrigeration Cooling Types & The Effect On Temperature
- How Do External Conditions Affect Internal Refrigeration Temperature?
- What Are the Different Types of Commercial Refrigeration Defrost?
- Explaining Thermostats & Temperature Displays in Commercial Refrigeration
- How Does Commercial Refrigeration Work?
- Do Temperature Fluctuations Make Frozen or Refrigerated Food Unsafe?
- Do Temperature Fluctuations Cause Icing Up or Misting/Fogging of Equipment?
- If Temperature Fluctuations Are Normal, How Do I Know If My Commercial Refrigeration Is Faulty?
- Why Do Commercial Refrigerator Condenser Coils Need To Be Cleaned?
- Brief Round Up of Key Points About Commercial Refrigeration & Temperature
- Refrigeration Temperatures FAQ's
Rather than spend an entire article explaining the science behind commercial refrigeration and it's relationship with temperature (other than the fact that it keeps things cold) before giving an answer, we'll do this differently.
Are temperature fluctuations in commercial refrigeration normal?
Most, definitely YES!
Now that's been cleared up, we can investigate why temperature fluctuations are a common feature of commercial refrigeration, how you know fluctuations are normal and when to recognise that there maybe an ulterior issue.
How Important Is Temperature In Relation To Commercial Refrigeration?
Maintaining the right temperature in commercial refrigeration is crucial for ensuring food safety, enhancing the quality of produce, and minimising waste, but can also improve energy efficiency and extend life span of equipment.
How Commercial Refrigeration Temperatures Promote Food Safety
The significance of temperature involves all aspects of storage, preparing, handling and cooking food, and each area must be closely monitored.
Temperature is a critical factor in ensuring food safety. Proper temperature settings are paramount to preventing food spoilage, inhibiting bacterial growth, and safeguarding the health of consumers.
Different food types, such as fresh meat, fresh fish, dairy products, fresh produce, frozen foods, beverages and ice cream demand specific temperatures to remain safe and fresh. Understanding the nuances of commercial refrigeration and temperatures and its impact on food safety regulations is essential for foodservice professionals.
Temperature plays a pivotal role in food safety, as improper temperature control can lead to bacterial growth and foodborne illnesses, jeopardising consumer health.
In particular, harmful bacteria such as Salmonella Enteritidis and Staphylococcus aureus thrive within specific temperature ranges, known as the food danger zone making it essential to maintain proper refrigeration. The process of blast chilling and blast freezing can significantly reduce potential safety issues and preserve food quality and safety. Failing to uphold and observe recommended storage temperatures, or blast chilling/freezing processes can result in:
- Rapid bacterial multiplication, leading to potential food poisoning or gastrointestinal issues in severe cases.
- Increased food spoilage, resulting in waste and financial losses.
By ensuring that refrigeration temperatures are adequately monitored and maintained, the risks associated with food safety can be significantly mitigated, ultimately safeguarding public health.
Improper temperature control in commercial refrigeration can lead to significant risks, not only in relation to food safety but also breaches of food safety regulations, which can have serious implications. When refrigeration systems fail to maintain the necessary temperatures, it not only threatens food safety but may also result in substantial economic losses including wasted inventory, fines for non-compliance and damaged reputation that can take years to restore.
Minimising Food Waste through Proper Temperature Control
Minimising food waste is a critical objective for businesses involved in food production and distribution, and one of the most effective ways to achieve this is through proper temperature control in commercial refrigeration systems.
Correct temperature settings are essential for enhancing food quality, as they help preserve flavour, texture, and nutritional value. By understanding the relationship between temperature settings and food spoilage, companies can significantly enhance their operational efficiency and reduce financial losses through lost stock.
Temperature significantly influences the shelf life of food items stored in commercial refrigeration, as both insufficient and excessive temperature conditions can accelerate spoilage and compromise food safety.
The importance of maintaining appropriate temperatures cannot be overstated, especially for raw meat and dairy products, which are particularly susceptible to bacterial growth when left outside of recommended ranges. Investing in reliable units specifically designed for purpose, whether for storage or display such as refrigerated fish keepers or meat serve over counters.
Proper food storage techniques include using airtight containers, avoiding overcrowding in refrigerators, and regularly monitoring temperatures with reliable thermometers is vital. Employing such measures can significantly extend the shelf life of various food types, contributing to both safety and waste reduction.
By adhering to guidelines, foodservice businesses can tackle food waste and ensure that their food remains safe, fresh, and enjoyable to consume.
In addition, the environmental burden of food waste cannot be understated: it leads to increased methane emissions when organic food waste decomposes in landfills. By maintaining optimal temperatures, businesses not only preserve their products but also contribute to sustainability efforts, thereby safeguarding the environment and enhancing their economic performance.
Why Correct Temperature Settings Can Improve Energy Efficiency
Implementing correct temperature settings in commercial refrigeration not only enhances food safety and quality but also significantly improves and promotes energy efficiency, resulting in lower operational costs for businesses.
Energy savings achieved through proper temperature management in commercial refrigeration can lead to substantial reductions in operational costs while ensuring food safety and quality.
By implementing accurate temperature settings, businesses can significantly lower energy consumption, which translates into noteworthy financial benefits. These savings can be redirected towards other essential areas of the business, such as upgrading equipment or enhancing marketing strategies, thus fostering a stronger business model with opportunities for growth and innovation.
How Temperature Settings Can Affect Equipment Lifespan
Maintaining proper temperature settings in commercial refrigeration not only impacts food safety and energy efficiency but also plays a crucial role in extending the lifespan of refrigeration equipment.
When equipment operates in optimal temperature ranges, it minimises the stress on components such as compressors and evaporators.
Extreme temperature fluctuations can lead to overworking, resulting in increased wear and tear.
Regularly checking settings and monitoring temperatures ensures that the equipment isn’t using more energy than necessary, helping to avoid unnecessary strain.
The basic principles of minimising temperature fluctuations and the amount of energy that is used to pull down temperatures within cabinets, in relation to the workload exerted on refrigeration components, can be used to demonstrate why most refrigeration units should not be turned off every night.
Please Note: some equipment for specific applications, such as soft scoop ice cream displays, should be switched off overnight.


The blue line shows that when the cooler is left running overnight to maintain a low temperature, the overall energy usage is much lower and less strain is placed on the components, meaning lower energy bills, less chance of mechanical failure and increased expected life span.
The red line shows that whilst there may be a drop in energy usage during the night, the extra power and strain on components imposed every morning means that overall energy bills will be higher and risk of component failure greatly increased.
Observing Correct Temperatures for Different Foods
Understanding that different food types require different temperatures in commercial refrigeration is vital for maintaining food safety and quality. Each category, from dairy products to fresh fish has unique temperature requirements that, if not adhered to, can lead to spoilage and foodborne illnesses. Read more about recommended commercial refrigeration storage temperatures for different types of food.
Commercial Refrigeration Cooling Types & The Effect On Temperature
When it comes to keeping equipment cool, commercial refrigeration works in multiple ways. Some types if cooling are better suited to specific types of equipment e.g. ventilated cooling better for gelato, static cooling for chest freezers. Understanding the difference between each cooling type, how they work, the advantages of each, their applications and the results they achieve in relation to the stored produce, is critical. Here we explain the three primary types of cooling: static, fan assisted, and ventilated cooling.
What's the Difference Between Static Cooling, Fan Assisted Cooling and Ventilated Cooling?
Static Cooling
Static cooling, also referred to as direct cooling, is a basic method of refrigeration where cooling is achieved through the natural circulation of cold air, without the use of mechanical fans.
This method relies on the principles of thermodynamics, where cold air sinks while warmer air rises, creating a convection cycle without the need for fans. Evaporator coils filled with refrigerant are located in the walls of the unit, (located in the shelves of some freezer models). The refrigerant in the coils absorbs heat from the air in the cabinet, during a heat exchange process. The cool air then gradually descends, replenishing the lower areas of the unit while pulling the warmer air upwards, thus maintaining a cold environment. This leads to the natural circulation of cold air.
As the air is not circulated with a fan, temperatures within the cabinet will vary depending on where the temperature is taken from. Typically or though not always, air will be slightly warmer at the top and colder at the bottom. In the case of some freezers where, coils may be located in the shelves which minimises the difference in temperature between the top of the equipment and the bottom. Static cooled equipment will generally require manual defrost (more on that later).
Pros & Cons of Static Cooling
Advantages:
- Simplified operation
- Low energy consumption
- Quieter than other cooling methods
Disadvantages:
- Coils positioned in walls (or shelves) make them inaccessible
- Freezers can experience ice build up
- Potential for uneven cooling between top and bottom of unit
- Slow pull down/chilling time
- Slower temperature recovery after door openings
- Requires regular manual defrosting
- Not ideal for high usage settings
What Types of Equipment Typically Use Static Cooling?
Static cooling systems are commonly, although not solely, found in equipment that is NOT in constant use or frequently opened, including:
- domestic refrigeration
- commercial chest freezers
- storage freezers
- ice cream displays
Fan Assisted Cooling
Fan assisted cooling is essentially in its most basic form, a static cooling system with the addition of a fan to circulate and distribute cold air.
The process of fan-assisted cooling involves the operation of an internal fan that actively circulates cold air throughout the refrigeration cabinet, allowing for improved temperature distribution and faster pull-down times than static cooled models.
By enabling an efficient air flow, the internal fan enhances the overall cooling efficiency of the system. This improvement not only promotes uniform temperature levels across all stored items but also minimises the risk of temperature spikes that can compromise food safety.
Pros & Cons of Fan Assisted Cooling
Advantages:
- More even temperature distribution than static cooled units
- Quieter operation than equipment that uses ventilated cooling
- More energy efficient than ventilated cooling
- Cheaper than units using ventilated cooling
- Manual and automatic defrost options
Disadvantages:
- Noisier than static cooling
- Takes longer to pull down temperatures than ventilated cooling
- Higher energy consumption than static cooled equipment
- More expensive than static cooled equipment
What Types of Equipment Typically Use Fan Assisted Cooling?
Fan assisted cooling is typically, but not solely used, in medium-sized equipment that experiences moderate-normal use in commercial settings, such as:
Ventilated Cooling
Ventilated cooling, also called dynamic cooling or fan forced cooling, offers a more advanced approach to refrigeration, using a fin type evaporator for more efficient cooling. The evaporator is typically positioned at the top of the equipment and is located behind a powerful fan that distributes chilled air evenly around the cabinet.
By constantly circulating air, it enhances the ability to regulate temperature fluctuations that can arise from frequent door openings or high item turnover. By ensuring a steady flow of air, the system effectively eliminates hot spots that can arise in more basic cooling systems.
While this method significantly boosts cooling effectiveness, it is essential to consider its energy consumption, as the increased airflow may lead to higher electricity usage.
Pros & Cons of Ventilated Cooling
Advantages:
- Ideal for high usage settings where doors are frequently opened
- Even temperature distribution
- Quickly pulls down temperatures, for faster cooling
- Uses automatic defrost
- Some sources believe that, when used optimally, it can manage moisture and humidity and prevent bacteria growth, however this is dependent on many other factors within the food hygiene and health and safety sphere and should not be taken as a silver bullet for protecting against issues arising from humidity and pathogens
Disadvantages:
- Louder than other types of cooling
- High energy consumption
- Expensive to buy
- Can lead to drying out of produce if it is not wrapped, packaged and stored correctly
What Types of Equipment Typically Use Ventilated Cooling?
Ventilated equipment is regularly used in high traffic environments where doors or lids are frequently opened. It is also the most effective solution for cooling larger equipment; the powerful fan evenly chilling larger areas and capacities. It will often be a feature of:
- multideck display fridges
- bottle coolers
- large storage fridges and storage freezers
- large display fridges and display freezers
- gelato displays
- cold rooms
- medical refrigeration
Static, fan assisted and ventilated cooling systems are also applicable with remote refrigeration systems, meaning that the perfect refrigeration is always available for every business.
How Do External Conditions Affect Internal Refrigeration Temperature?
While there are static, fan assisted and ventilated cooling types of refrigeration to regulate internal temperatures of units, this alone doesn't mean that precision temperatures will definitely be achieved or the equipment perform as expected. The external ambient conditions, referred to as the Climate Class, of the shop, kitchen, bar or storage room etc. where the equipment is placed will also affect internal temperatures. But what does Climate Class mean? In it's most basic explanation, it incorporates the temperature of the location around where equipment is positioned and the humidity of the environment, both of which will directly affect performance and the cabinets ability to hold produce at safe temperatures.
What Are the Different Types of Commercial Refrigeration Defrost?
In commercial refrigeration, understanding the types of defrost is crucial for maintaining optimal cooling processes and enhancing equipment performance. This includes manual defrost, which requires operator intervention, and various automatic defrost methods, such as hot gas defrost, electric defrost, off cycle defrost, and water defrost.
Each method plays a significant role in managing ice build-up and ensuring energy-efficient operation of refrigeration systems, while also influencing the refrigeration cycle and extending the equipment lifespan. When defrost cycles are active, you may notice greater temperature fluctuations, however this should not compromise the safety of stock.
Explaining Thermostats & Temperature Displays in Commercial Refrigeration
Two primary types of thermostats are used in commercial refrigeration: mechanical controllers, which rely on mechanical components such as temperature sensors, a temperature sensing cavity and contact switches, and digital controllers with more sensitive sensors and circuit boards, which offer high control precision and advanced features for monitoring and adjustment.
Each type has distinct advantages and applications, making it essential for businesses in the food industry to select the appropriate thermostat for their refrigeration systems based on their specific temperature requirements and operational needs.
Mechanical Thermostats
How Do They Work?
A temperature sensing tube, or 'capillary tube' filled with gas, senses thermal expansion and pressure generated in the sensing cavity. This tube then triggers a contact switch which controls the start and stop of the commercial refrigeration compressor.
What Does This Mean for Temperatures?
While effective, the operation of these thermostats can sometimes lead to limitations regarding control precision. For instance, manual thermostats are typically controlled through a simple dial leading to less accuracy in settings.The lack of electronic components can also cause a noticeable delay in response times, leading to potential inaccuracies in temperature regulation.
In specific refrigeration applications, addressing the defrosting function is crucial. Mechanical thermostats may not be able to manage defrost cycles as precisely as digital alternatives, risking frost build-up and impacting the system's efficiency.
Ultimately, while mechanical thermostats serve essential roles in temperature regulation, users should be aware of their limitations and explore other options for improved precision.
Digital Thermostats
How Do They Work ?
A temperature sensor detects the temperature of air inside the equipment. This then prompts the circuit board to control the start or stop of the compressor. It is generally 'return air' that is monitored as this is when refrigerated air is at it's warmest.
What Does This Mean for Temperatures?
Digital thermostats represent a modern solution for temperature control in commercial refrigeration, offering high control precision through the use of advanced electronic components and sensors that monitor the temperature in real-time.
These more sophisticated thermostatic devices are more responsive than mechanical thermostats and can provide greater accuracy in temperature adjustment ensuring that refrigeration systems maintain consistent conditions, reducing wear and tear on equipment and ultimately leading to significant energy efficiency improvements.
Capable of offering real time temperature monitoring of air within the equipment, sensors can respond more quickly to temperature fluctuations.
Digital thermostats can manage defrost functions with default settings typically set to cycle between 2 and 4 times a day. The defrost cycle frequency and duration may vary depending on the type of equipment the brand so it is advised to always refer to the user manual.
The Accuracy of Mechanical & Digital Thermostats in Setting & Monitoring Temperatures in Commercial Refrigeration
The accuracy of thermostats, whether mechanical or digital, is vital for effective temperature control in commercial refrigeration, as it directly influences food safety and compliance with health regulations.
Mechanical Thermostat Accuracy
Mechanical thermostats may struggle with inaccuracies due to their reliance on physical components and environmental factors, leading to unstable temperatures.
This reduction in accuracy can be attributed to a variety of factors, including thermal lag, which occurs when there is a delay in the thermostat's response to temperature changes. It is essential to understand that the location of the thermostat within the unit can significantly influence its ability to gauge actual temperatures accurately.
External conditions such as the ambient temperature and humidity levels can further complicate matters, leading to potential food safety issues.
Addressing these issues by implementing regular maintenance and calibrating thermostats can help ensure a more stable temperature environment, ultimately preserving food safety.
Digital Thermostat Accuracy
Digital thermostats offer superior accuracy and control precision, enabling precise temperature adjustments and consistent monitoring of the temperature range required for various food products. This accuracy is essential for maintaining optimal storage conditions and meeting industry standards.
As temperatures are set via buttons combined with a digital numerical display, users have greater visual awareness and accuracy indication of settings.
Depending on the application of the thermostat and the quality of the technology, some digital thermostats will allow for programming and alerts for temperature fluctuations outside of normal range. This will typically be a feature on medical chillers where accuracy is critical.
The majority of automatic defrost units use digital controllers to increase automation of the equipment's operation.
The Truth About Thermostat Accuracy
As previously established, temperature readings and accuracy will vary depending on whether equipment uses mechanical or digital thermostats and controllers. No equipment will give entirely pin point precision readings, however medical refrigeration will report with more accuracy and precision due to the sensitive nature of the pharmacy fridge or pharmacy freezer contents.
Furthermore, few people realise that:
while temperature displays give an indication of the interior temperatures of the cabinet, it in no way reflects the temperature of the produce within.
Product, whatever it is, will take longer to chill or freeze than the cabinet itself due to the density and mass of food and drink compared with air. The only accurate way to measure the core temperature of products for food safety is to use an internal or core temperature probe.


Top Tip: It is recommended to invest in a second thermometer which should be located in a different zone of the refrigeration to where the integrated thermostat is. Multiple readings from different places within the unit is advised to ascertain effective air circulation and even temperature distribution.
Monitoring Cabinet Temperatures
You may notice minor variations in general cabinet temperature in different areas of the equipment depending on the type of cooling system. By taking multiple readings you can create a broader idea of temperature ranges around the cabinet. Note that while food temperatures when probed should stay consistent across any application, static cooling units will have more temperature variation within the unit than fan assisted or ventilated equipment.
Monitoring Core Food Temperatures
Core internal temperature probes are also recommended for produce in commercial kitchens to maximise food safety. To avoid unsightly holes created by temperature probes in produce such as chickens or other meats, where the aesthetics of the product are under scrutiny, some chefs choose to use a sample piece of produce, such as a block of butter for example, to give an indication of the core temperature of other produce within the equipment. As the block of butter will be used in the cooking and not be served whole, the indent left by the temperature probe won't cause any problems visually.
This action mimics an element of the official testing process carried out by manufacturers when determining the Climate Class of equipment. During this test of core produce temperatures, they load refrigeration with bricks or packs (referred to as M-Packs aka measurement package) each containing a core temperature probe within a Tylose gel. This gel mimics the properties of lean beef making it ideal for more accurate food safety temperature testing. Each probe sends readings of internal temperatures throughout the entirety of the testing duration. Under M-Pack testing conditions, core temperatures are monitored when refrigeration is subjected to typical frequency of use to determine if core food temperatures remain safe.
Monitoring equipment and food temperatures for HACCP (Hazard Control and Critical Control Points) records are vital in foodservice businesses to identify potential hazards and set out a clear process to correct or eradicate the issue.
Why Use Secondary Thermometers?
Using a secondary, independent thermometer can help to create a more complete picture of storage temperature records. Additional recordings can be taken using manual food thermometers within the cabinet or alternatively, via remote temperature recording systems which digitally record temperatures, usually via WI-FI connection. Some equipment will take measurements at frequent intervals, some equipment will use continuous monitoring of temperatures.
This process, sometimes referred to as temperature mapping, thermal mapping or temperature logging, involves the system taking readings from precision sensors at predetermined, programmable intervals, all information being recorded digitally. It may also allow you to set alarms to notify if temperatures within the cabinet rise or fall above or below the set range. This is perfect for optimising food safety should the door accidentally be left open, or settings incorrectly changed.
If employing manual recording equipment, manual logging sheets must be completed and filed with HACCP data for future reference. Remote monitoring systems will record data digitally for ease.
How Does Commercial Refrigeration Work?
Rather than delve into the mechanics of how the refrigeration system works, it's important to consider a different aspect of how commercial refrigeration operates. This involves understanding not how refrigeration generates cold temperatures but how it maintains these temperatures.
Firstly, when you set the thermostat to a specific temperature, the equipment does not operate only at that setting. Compressors don't get to the desired temperature and then decrease power to hold the environment indefinitely, minutely controlling the conditions to achieve the exact settings consistently.
Commercial refrigeration operates within a temperature range around the temperature that has been set, but not consistently at the temperature that it has been set to.
Refrigeration will have a preset or predetermined differential e.g. 3° - this deviation may vary between equipment and manufacturer. Refrigeration will chill equipment to the set temperature and then switch off. Once the unit has risen in temperature by the differential, the refrigeration system will kick in again and pull temperatures back down to the set temperature.
Check out this simple illustration:
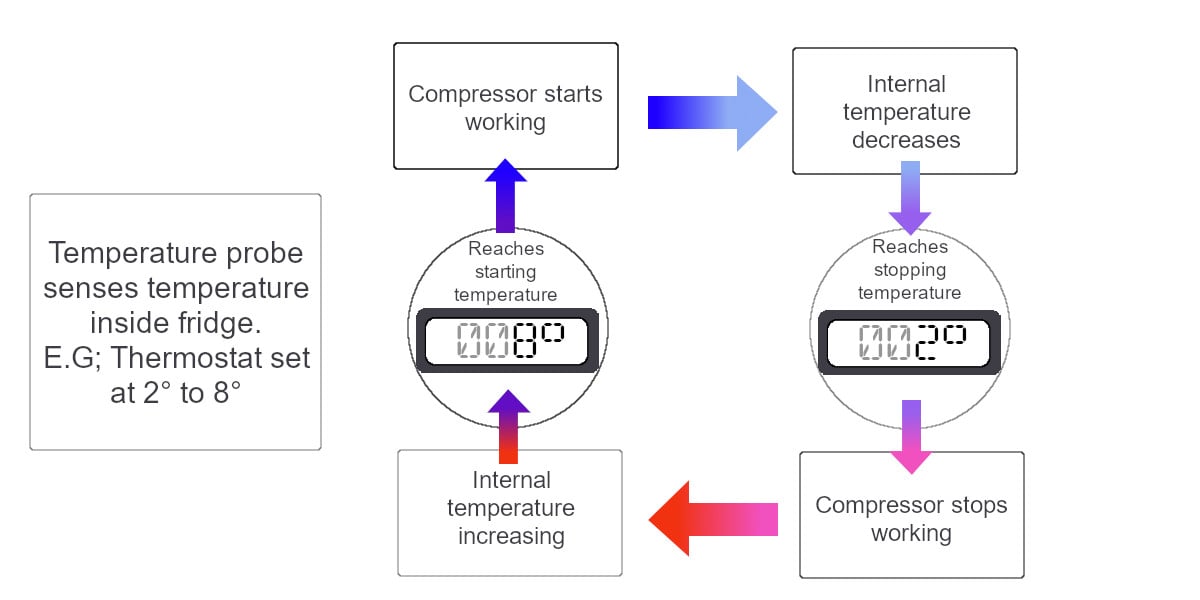

So, why does commercial refrigeration work in this way?
Operating in this way can extend the life span of equipment and reduce energy consumption by exerting less stress on refrigeration components.
Do Temperature Fluctuations Make Frozen or Refrigerated Food Unsafe?
Temperatures will generally fluctuate by 3° above or below the set temperature. This difference will not compromise food safety or quality. Commercial refrigeration is built with high quality insulation that can hold the conditions within a cabinet at a consistent temperature, whether the thermostat is showing minor fluctuations or not.
This insulation works on a similar principle to that of domestic fridge freezers, in that during a power cut your home freezer can remain frozen when the door is kept closed for hours and typically longer. Commercial refrigeration uses better quality materials and insulation meaning that minor fluctuations that are the normal for commercial equipment and intrinsic to how all commercial refrigeration works, have no effect on produce or performance.
Once stock has achieved optimum core temperature, minor fluctuations in air temperature, such as those experienced during normal operation, will not undermine the safety and quality of stock. Only if the door is left open for extended periods, there is no power to the unit or temperatures are too high for an extended period of time, will food possibly be affected.
Do Temperature Fluctuations Cause Icing Up or Misting/Fogging of Equipment?
Refrigeration essentially works by drawing moisture out of produce, replacing it with cold air - that's why when you put open/unwrapped food in a fridge it shrivels. Due to this, some degree of ice, mist, fog or condensation is entirely normal, especially when you factor in the basic science, that when cold and warm air meet, they create condensation, mist or fog.
If you turn on a commercial fridge or freezer with nothing in it, leave it to get to temperature and open the door there will be no ice or condensation as there is nothing with moisture to draw out. If you fill those cabinets with produce and repeat, there will typically be a little condensation or frosting as the moisture is drawn out of produce, settling on the closest surface to warm air (typically lids, doors, walls). Moisture and some degree of ice/frost is natural with any equipment, however the level of condensation/frost that you experience may depend on the type of cooling system, the type of defrost and the products you are putting in the unit. Read more about tackling excessive levels of condensation in display refrigeration.
If Temperature Fluctuations Are Normal, How Do I Know If My Commercial Refrigeration Is Faulty?
We've ascertained that temperature fluctuations are entirely normal, but how do you know when changes in temperature are expected or something that require further investigation?
Other than the variations experienced during typical operation, fluctuations will also occur, and are to be expected, during:
- stocking of equipment,
- defrost cycles,
- if doors are not shut properly,
- during busy services or periods when doors are being frequently opened.
If doors are closed, stock is down to temperature and the unit is not being opened, the temperature should stabilise and return to normal differential range.
High Temperatures That Are Not A Result of Recent Activity or Use
If equipment is consistently registering at high temperatures even when doors have been shut, the unit has not been restocked, hot or warm foods have not been put in, the unit is being used to chill or freeze the products that it was intended for (i.e. drinks NOT FOOD in drinks fridges) or you notice produce spoiling quickly or releasing unexpected odours etc. then you may need to make further checks.
Areas to Check When Refrigeration Is Not Getting Down to Temperature
- Are door seals and gaskets intact and creating a tight seal? Faulty or ill-fitting seals can result in warm air getting into equipment and cold air escaping.
- Are condensers and vents clear of dust and debris? Read more about the importance of cleaning condenser coils.
- Is there ample airflow around the exterior of the unit? Refrigeration emits heat due to the refrigeration process and so a 5-10cm air gap is recommended around equipment to allow it to breathe.
- Is the unit overstocked? Ample airflow within the equipment is just as important as exterior airflow.
- Are the ambient temperatures of the room within the limits of manufacturers recommendations? Is equipment in direct sunlight or in the path of air conditioning systems? Direct sunlight can raise ambient temperatures meaning that refrigeration components are under more stress to pull down temperatures. In the case of equipment such as multidecks that have an open front, air conditioning can disrupt the path of the airflow that the equipment relies on to create an air curtain to contain cold temperatures.
- Faulty/malfunctioning thermostat and/or other electro-mechanical faults? Check equipment temperatures using a manual or digital thermometer to verify readings from the actual equipment thermostat. If this also shows disparity between temperature settings and the actual temperature, get in touch with your commercial refrigeration supplier and ask them to arrange for an engineer to attend site.
Read more about Common Commercial Refrigeration Problems and What Users Should Check.
Why Do Commercial Refrigerator Condenser Coils Need To Be Cleaned?
It is common knowledge that cleaning and maintenance is a massive part of using any commercial refrigeration. While this may be carried out frequently with regards to the interior of the unit in regard to food safety and hygiene, there are users who neglect the fundamental parts, such as door seals, and the actual functioning components of the equipment, especially condenser coils, that ensure optimal refrigeration performance.
Commercial refrigeration condenser coils are essential components in the refrigeration system that play a crucial role in heat dissipation, allowing the entire system to operate efficiently. These coils are responsible for releasing the heat absorbed from the refrigerant as it circulates through the system, ensuring optimal temperature management for business operations.
If condenser coils are dirty or covered in dust, they can significantly hinder the performance of the commercial refrigeration system. Dirty or blocked condenser coils lead to reduced cooling efficiency, making it challenging for commercial refrigeration systems to maintain desired temperature levels, which can negatively impact food quality and safety. Dust and debris on coils restricts the necessary airflow required to dissipate heat from the equipment, leading to inconsistent temperatures within the equipment. Dirty condenser coils can also lead to increased energy consumption and risk of equipment failure.
Is There A Difference Between Cleaning & Maintaining an Integrated Fridge or Freezer to a Remote Unit?
As already established, cleaning and maintenance is vital for any commercial refrigeration, whether it uses integrated cooling systems or remote refrigeration. While integral, integrated or self-contained refrigeration will house all of the essential cooling components within the unit itself, remote systems will have the condensing unit located elsewhere, typically on external walls of the building. Read more about Remote Vs. Integral Commercial Refrigeration.
Although remote refrigeration components may be laid out and situated differently to integrated units, they still require cleaning and maintenance. While it is a relatively easy task to access components in integral units, remote systems pose a little more difficulty. Maintenance and cleaning of remote units will typically fall under your business's Planned Preventative Maintenance (PPM) schedule and will need to be carried out by qualified engineers.
Brief Round Up of Key Points About Commercial Refrigeration & Temperature
- Moderate temperature fluctuations in commercial refrigeration, typically 3° differentials, are entirely normal and will not have a detrimental effect on stock quality or food safety.
- The type of cooling system your equipment operates, will determine the degree of fluctuation and temperature accuracy at different points around the unit. Static is the most basic cooling system that experiences more variation in temperatures, fan assisted or ventilated, offer more even cooling, however all have pros & cons.
- Mechanical thermostats and controllers are not as accurate as digital thermostats and controllers.
- Temperature displays reflect the temperature of the air within the cabinet, not the temperature of produce. Core temperature probes are recommended if precise internal temperatures are required.
- A degree of condensation and mild ice are to be expected in commercial refrigeration due to the basic concept of thermodynamics when cold air meets warm air. Excessive quantities of condensation, ice, fogging or misting may be due to improper use, unsuitable positioning of equipment or an alternative issue with the unit which may require an engineer.
- Greater temperature fluctuations are normal when restocking equipment, during busy periods when doors are frequently opened and during defrost cycles.
Look after your commercial refrigeration. Cleaning and maintaining equipment including the main refrigeration components can ensure less strain on motors, better efficiency and overall more consistent performance.
Refrigeration Temperature FAQ's
Why does my commercial refrigeration temperature fluctuate?
Commercial refrigeration will generally not hold temperatures consistently to the degree that it is set. Due to the very nature of the way that refrigeration systems work, temperatures will vary within typically within a 3°C range. Contributing factors include the type of cooling and the type of thermostat equipment uses, ambient temperatures and positioning of equipment, the items being stored and general level of cleaning and maintenance.
Are temperature fluctuations in my commercial fridge and freezer unsafe?
No. In relation to food, when stock has reached recommended core temperatures, any minor fluctuations due to normal use, should not affect the core temperatures of food and will therefore maintain food safety. High quality insulation means that units can maintain consistent temperatures within the cabinet, even when thermostats show minor fluctuations.
What's the difference between refrigeration cooling types?
Commercial refrigeration will generally use either static cooling, fan assisted cooling or ventilated cooling. Static cooling relies on the natural circulation of cold air within the equipment. Fan assisted cooling is essentially uses a static cooled base with the addition of a fan to circulate cold air. Ventilated cooling uses a fin type evaporator, with the evaporator positioned behind a powerful fan at the top of the unit where air is coldest, to distribute chilled air around the cabinet evenly.
What type of thermostat does commercial refrigeration use?
Commercial refrigeration will use either a mechanical thermostat or a digital thermostat. Mechanical thermostats are less accurate at measuring temperature than digital thermostats.
Why does my refrigeration show a different temperature to what it is set to?
Temperatures will generally fluctuate within a 3°C range as the compressor adjusts. Temperatures are typically measured via a capillary tube filled with gas which expands with heat in the case of mechanical thermostats, and via measuring of the warmer air returning to the thermostat, in the case of digital thermostats. This means that temperatures displayed are not actually representative of the air in the overall cabinet.
Do I need to use an extra thermometer for commercial fridges?
While not strictly required, using a second thermometer helps to gain an overall more comprehensive log of temperatures. You may want to place a secondary thermometer within the equipment itself to measure air temperature or, alternatively, use a food temperature probe to measure core temperatures of stock to ensure food safety while in the equipment.
What typically causes commercial refrigeration temperature fluctuations?
Temperature fluctuations, other than those occurring during the natural compressor cycle, will typically be experienced when stocking equipment, during defrost cycles, during busy services or periods when doors are frequently being opened and if doors are not shut properly.
How do I know if my commercial refrigeration is faulty?
If you are experiencing high temperatures or large fluctuations (greater than approximately 3°C) and the doors have been shut properly for an extended period, you are using equipment for the purpose it is designed (drinks, not food, in drinks fridges), or units are not in the middle of a defrost cycle, then it may signal that there may be an issue. Check door seals and gaskets are intact, internal and external airflow around the equipment is adequate, condensers and vents are clear of dust and debris, and that ambient temperatures are suitable. If there are no issues in these areas then contact your commercial refrigeration supplier and an engineer can be arranged to attend site.







Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *