
Refrigeration is an important aspect of both domestic and commercial food management. The creation of the first modern fridge in the late 1800's was an ushering of a great era in the food preservation and foodservice world. This has further been advanced by new technology which has seen a current production of more than 1 billion refrigerators around the world.
The main reason catering fridges are used in businesses and domestic alternatives at home, is to keep food cold. Fridges are important because food stays fresh for longer, thus helping cut down wastage in foodservice settings. They also help increase profits in businesses by maintaining the quality of food for a longer time and allowing chefs the time and opportunity to create their best foods.
As the production of highly perishable foods has increased, so has the need for storage solutions that can preserve foods for longer and prevent wastage and unwanted loss. Even though refrigeration is an important part of our lives, many people still don't understand how it achieves the desired results and are left wondering, how does a refrigerator work and how does it maintain such cold temperatures for a long time?
The Refrigeration Cycle Components
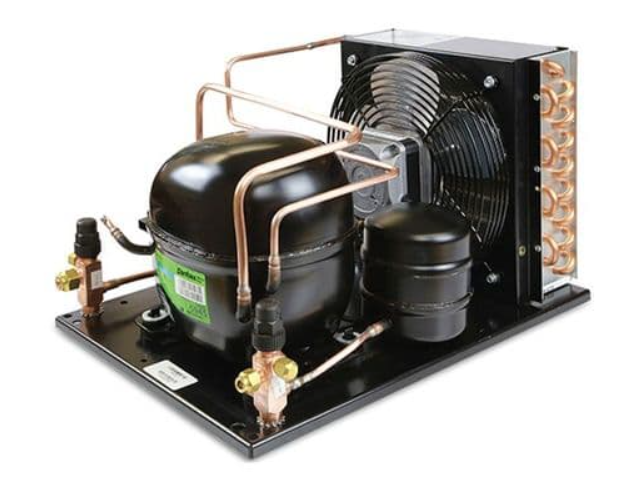

A standard refrigerator will have mechanical elements that make it easy for it to achieve and maintain cold temperatures. They are the components that will maintain the refrigeration cycle. These essential elements are at the core of domestic models and commercial refrigeration such as display fridges. These components are highly specialised in order to provide the desired effects.
They include a compressor, condenser, expansion valve/metering or throttling device and an evaporator. Additionally, the fridge has to use a refrigerant, a substance that is used to provide the cooling effect. The refrigerant has to pass through all these components and in each, it is altered to achieve the required temperatures.
These individual parts all work together within commercial fridges and freezers with an integral system. In remote refrigeration systems these components may be positioned separately but still function as a single system. Let's break down each individual segment to see the role they play during the complete cycle.
Compressor
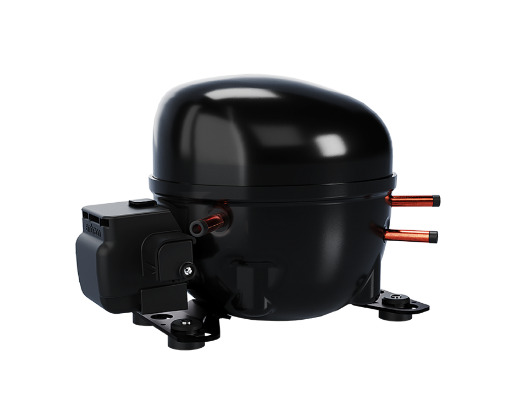 Its work is to control the flow of the refrigerant by acting as a motor and a pump. This allows it to pressurise the refrigerant and reduce its volume.
Its work is to control the flow of the refrigerant by acting as a motor and a pump. This allows it to pressurise the refrigerant and reduce its volume.
There are five types of compressors used in both commercial and domestic refrigerators. They include reciprocating, rotary, screw, centrifugal and scroll. Of the five, the reciprocating compressor is the most commonly used in home and commercial kitchen refrigerators.
Condenser
The condenser works by condensing the refrigerant. The refrigerant entering the condenser is hot and pressurised. This heat must be ejected from the equipment, which is why the back of refrigeration will be warm and emit heat. The condenser cools the refrigerant by converting it into a liquid state.
There are three types of condensers.
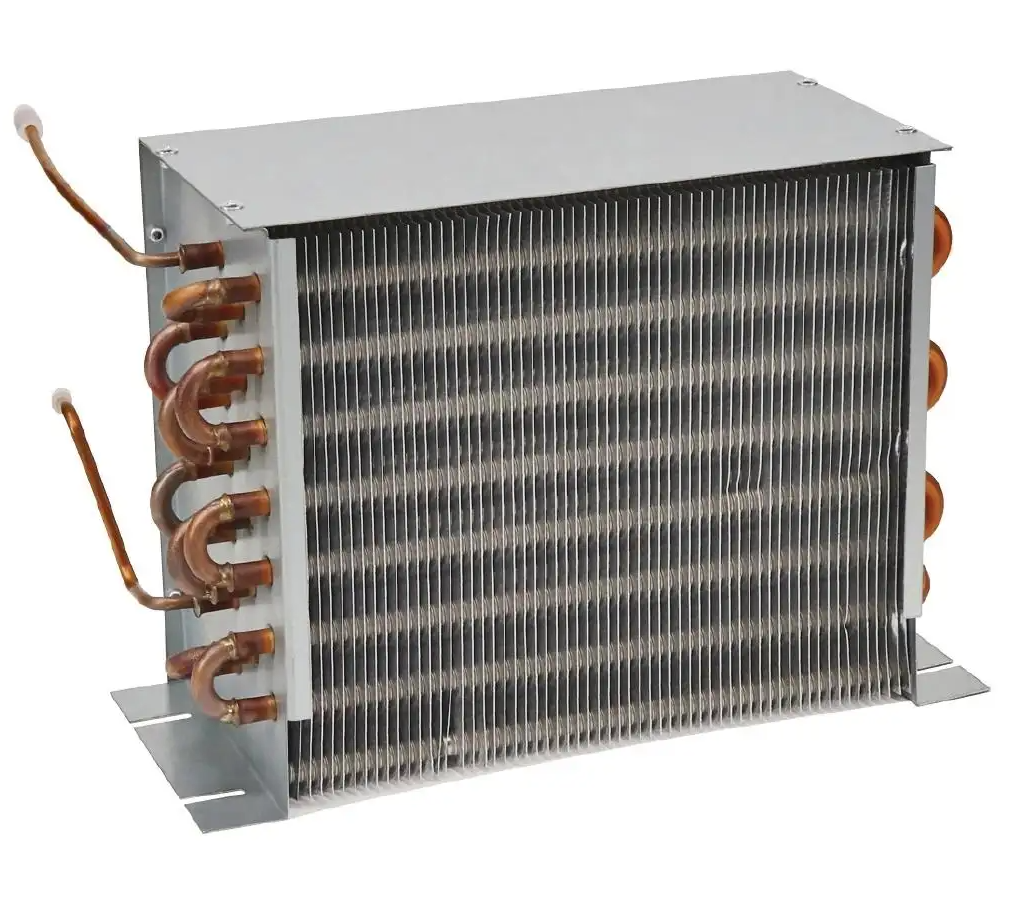 Air-cooled. you will find this in smaller refrigerators such as the ones used at home. They are ideal when the refrigerant quantity is small. The air-cooled condenser is also called coil condenser because it comes with aluminium or copper coils at the back of the fridge. The coils increase the surface area for cooling the refrigerant.
Air-cooled. you will find this in smaller refrigerators such as the ones used at home. They are ideal when the refrigerant quantity is small. The air-cooled condenser is also called coil condenser because it comes with aluminium or copper coils at the back of the fridge. The coils increase the surface area for cooling the refrigerant.
Air-cooled condensers are further divided into two. The natural convection condenser which uses the natural flow of air to cool the refrigerant and the forced convection condenser which uses a fan to draw in cold air.
Water-cooled condensers. These are used in large plants where there is more refrigerant. They use water to provide the cooling effect on the refrigerant. Water-cooled refrigerants are further subdivided into three.
- Tube-in-tube or double pipe type
- Shell and coil type
- Shell and tube type
Water-cooled systems typically work better when operating in higher ambient temperatures.
Evaporative Condensers. These are used in ice plants and are a combination of water-cooled and air-cooled condensers. As such, they come with benefits from both types of condensers.
What is a remote condenser? Where remote refrigeration systems are used, the condenser is the part that can be seen outside of buildings. This component is typically positioned on outdoor walls or roofs.
Expansion Valve
 The expansion valve helps reduce the pressure and temperature of the refrigerant. The sudden drop in pressure and temperature produces a cooling effect.
The expansion valve helps reduce the pressure and temperature of the refrigerant. The sudden drop in pressure and temperature produces a cooling effect.
The expansion valve is a metering device that regulates the amount of refrigerant used in meeting the load requirements. The load, in this case, are the products that need cooling in the refrigerator.
There are various types of expansion valves. They include:
- Capillary Tube
- Constant Pressure or Automatic Throttling Valve
- Thermostatic Expansion Valve
- Float Valve
Evaporator
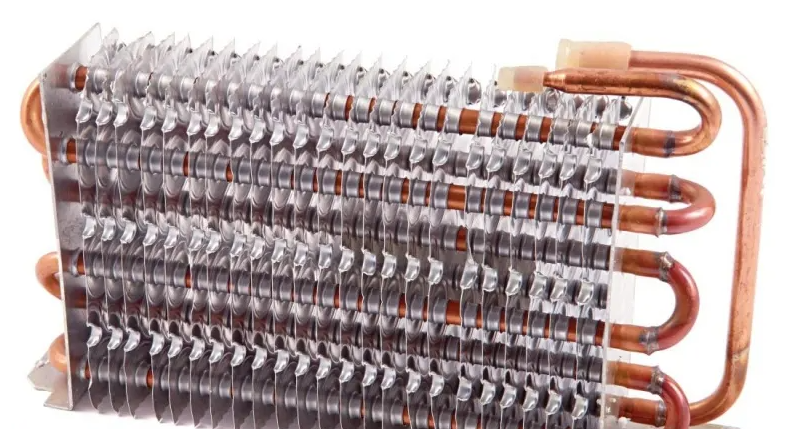 The evaporator absorbs heat inside the refrigerator. It acts as a medium of exchange for heat from the stored products (load) to the refrigerant. In most cases, the evaporator is the coldest part of the fridge or the freezer.
The evaporator absorbs heat inside the refrigerator. It acts as a medium of exchange for heat from the stored products (load) to the refrigerant. In most cases, the evaporator is the coldest part of the fridge or the freezer.
Here, the refrigerant is cold and moves at a slower pace in order to absorb as much heat as possible from the load. As it absorbs the heat, it gets hotter and turns into a gas. By vaporising the refrigerant more heat is absorbed from the load. The refrigerant, now hot and in gaseous form, is then pushed back into the compressor.
The evaporator in remote refrigeration systems is situated in the actual equipment or, in the case of air conditioning, inside the room being cooled.
In commercial refrigeration such as bottle coolers, these core components are manufactured to work harder to withstand heavy duty use and increased demand.
The Refrigeration Cycle
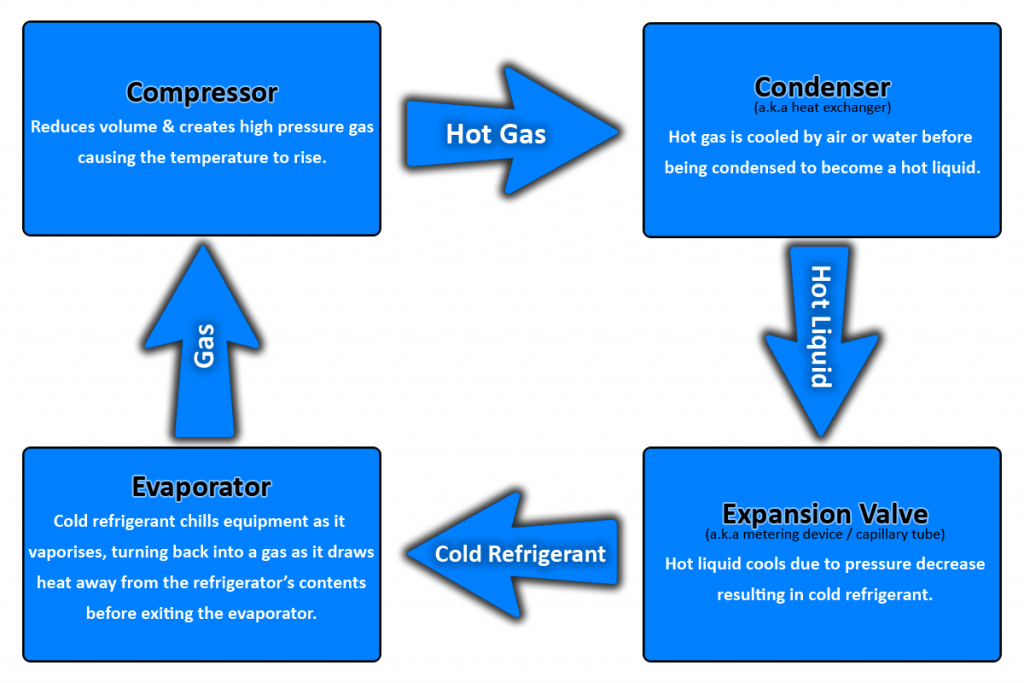 The refrigeration cycle starts and ends with the compressor. The refrigerant flows into the Compressor where it is compressed and pressurised. At this point, the refrigerant is a hot gas. The refrigerant is then pushed to the Condenser which turns the vapour into liquid and absorbs some of the heat. The refrigerant then proceeds to the Expansion Valve where it expands, losing pressure and heat.
The refrigeration cycle starts and ends with the compressor. The refrigerant flows into the Compressor where it is compressed and pressurised. At this point, the refrigerant is a hot gas. The refrigerant is then pushed to the Condenser which turns the vapour into liquid and absorbs some of the heat. The refrigerant then proceeds to the Expansion Valve where it expands, losing pressure and heat.
The refrigerant coming out of the expansion valve is cold and slow due to the loss of pressure. It enters the Evaporator in a liquid state where the exchange of heat takes place thus cooling the load inside the refrigerator. As the gas cools down the load, it absorbs the heat which turns it into a gas. The gas is then pushed back into the Compressor where it can start the cycle again.
During the refrigeration cycle, a build-up of ice around the evaporator may occur. Both commercial fridges and catering freezers will combat this build-up with some form of defrost system. Read more about different types of defrosting function here.
What Is Refrigerant?
 Refrigerant is the substance that flows around the refrigeration system and cools equipment. It changes from liquid to gas depending on the temperature and whether it is absorbing heat or cooling down. All refrigeration, air conditioning or other cooling equipment will require a refrigerant. There are different types of refrigerant available, each with different properties. The preferred and recommended refrigerants have changed over the years with the advancement in scientific research and understanding of the effects on the environment leading to the introduction of the F-Gas Regulations. With every business needing to adhere to this legislation, it has directly impacted the commercial refrigeration industry. This guide on F-Gas Regulations breaks down that impact.
Refrigerant is the substance that flows around the refrigeration system and cools equipment. It changes from liquid to gas depending on the temperature and whether it is absorbing heat or cooling down. All refrigeration, air conditioning or other cooling equipment will require a refrigerant. There are different types of refrigerant available, each with different properties. The preferred and recommended refrigerants have changed over the years with the advancement in scientific research and understanding of the effects on the environment leading to the introduction of the F-Gas Regulations. With every business needing to adhere to this legislation, it has directly impacted the commercial refrigeration industry. This guide on F-Gas Regulations breaks down that impact.
Understanding the Refrigeration Cycle
The refrigeration cycle basically involves the movement of refrigerant from one place to the next and in different forms with the ultimate goal of pulling down temperatures whether in a cabinet, counter or even cold room format. The one main importance of learning how your commercial fridge works is so that you understand how to clean and maintain equipment effectively. For example, understanding that your fridge uses an air-cooled condenser will help you find the ideal position for your unit in order to make its work easier and lower the energy consumption. By understanding the basics, only then can one fully benefit from their commercial refrigeration.







Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *